
Safety Glass plays a crucial role in our daily lives. From homes to workplaces, the right type of safety glass can prevent injuries. Whether you're renovating or building new spaces, understanding safety glass types is essential.
Different settings require different glass types. Laminated glass, for example, is commonly used in vehicles for its durability. It holds together when shattered, minimizing harm. Tempered glass, on the other hand, is known for its strength under pressure and heat.
Choosing the appropriate safety glass can be daunting. Many people overlook essential factors like thickness and resistance ratings. Mistakes can lead to financial losses or even injuries. Ensuring that you select the right type requires careful consideration and a bit of research. Stay informed, and you’ll make better choices for your safety and peace of mind.
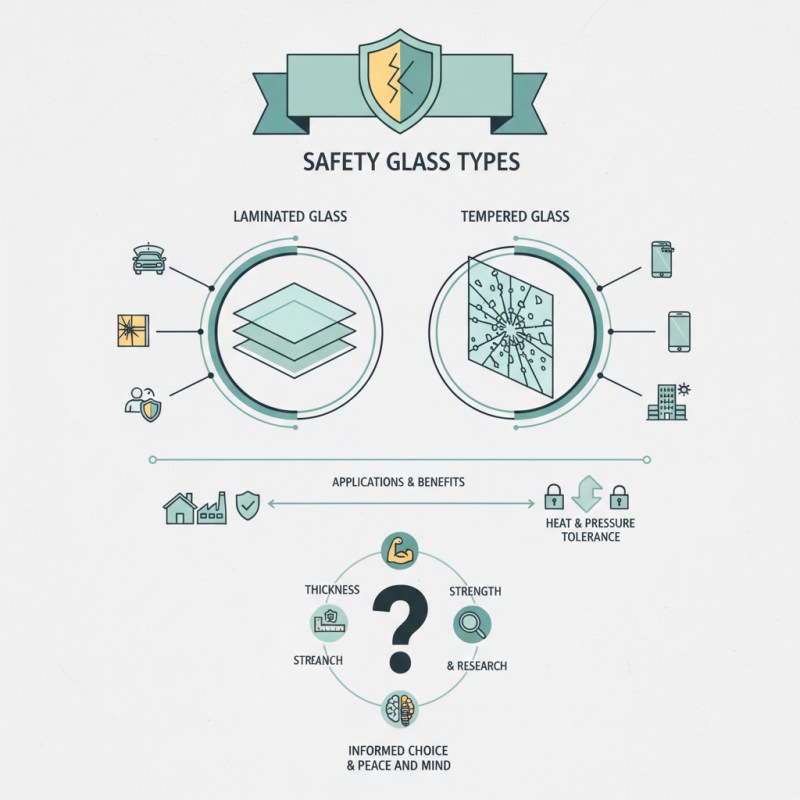
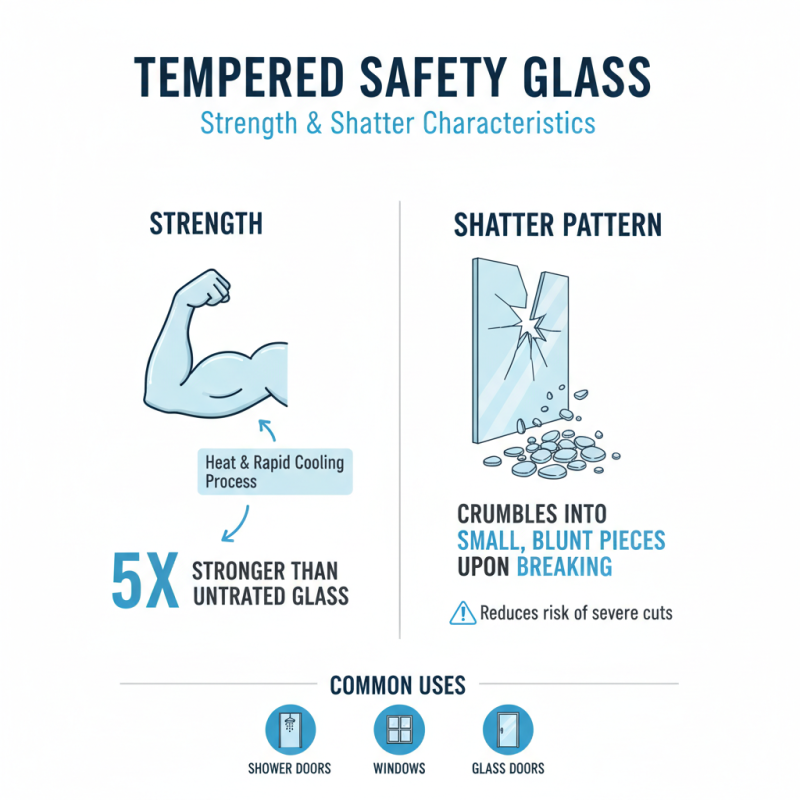
When considering safety glass, several types stand out for their unique characteristics and applications. Tempered glass is known for its strength. It undergoes intense heating and cooling, making it four to five times tougher than untreated glass. This type is ideal for shower doors, glass doors, and windows. However, when broken, it shatters into tiny pieces, which can pose risks.
Laminated glass consists of layers of glass and a plastic interlayer. This combination absorbs impact energy and keeps the glass intact when shattered. It's often used in car windshields and skywalks. A downside is its weight, which can add to installation challenges.
Tips for choosing safety glass: always assess the environment where it will be installed. In high-impact areas, laminated glass is a better choice. Additionally, consider the aesthetics. Tempered glass offers a sleek look while laminated glass can provide UV protection. Remember, the safest option may not always be the lightest. Weighing features against practical needs is key.
Another popular option is polycarbonate glass, known for its incredible impact resistance. It can withstand blows that would break other types. Polycarbonate is used in applications like safety glasses and prison windows. However, it can scratch easily, which affects visibility. It's essential to weigh both safety and maintenance aspects before selection. Always think critically about what suits your specific needs best.
When comparing tempered and laminated glass, durability is a key factor. Tempered glass undergoes a heating and cooling process. This makes it much stronger than standard glass. If broken, it shatters into tiny pieces. This reduces the risk of serious injuries. However, this also means it can break unexpectedly under heavy impact.
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers bonded with a plastic interlayer. This design holds the layers together even when shattered. It provides more safety during incidents like an accident. Yet, it may not withstand extreme impacts as well as tempered glass. Over time, the adhesive can degrade. This raises concerns about the longevity of the product.
Damage to laminated glass may not be as visible. Small cracks or deformations can go unnoticed. Regular inspection is essential to maintain its integrity. Ultimately, both glass types have their strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these can help in making informed choices for safety applications.
Polycarbonate is a crucial material in safety glass solutions. It offers strength and resilience, making it a popular choice for various applications. This thermoplastic is lightweight yet highly impact-resistant. Buildings, vehicles, and sports equipment often employ polycarbonate glazing for enhanced safety.
When choosing safety glass, consider these tips. Assess the environment where the glass will be used. For high-impact areas, polycarbonate provides superior protection. It’s also essential to evaluate thickness. Thicker panels typically offer better safety but weigh more. Balancing safety and weight can be tricky.
Maintenance is another key factor. Polycarbonate can scratch more easily than tempered glass. Regular cleaning is necessary, but harsh chemicals should be avoided. Using a soft cloth with mild soap can help preserve the surface. Remember, optical clarity is vital, especially for larger panes. Investing time in proper care will extend the life and effectiveness of safety glass.

Safety glass technologies are essential to meet industry regulation requirements. These regulations aim to protect people in environments with potential hazards. According to data from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), about 20% of workplace injuries involve glass-related incidents. This statistic emphasizes the need for robust safety glass solutions.
Several types of safety glass, such as tempered and laminated glass, meet these safety standards. Tempered glass is heat-treated, making it five times stronger than regular glass. When it breaks, it shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing injury risks. Laminated glass, on the other hand, consists of layers of glass with an interlayer that holds fragments together. A report from the Glass Association states that laminated glass can absorb up to 90% of the impact energy. Yet, despite technological advances, some products fail to pass rigorous testing.
Industry standards, like those set by OSHA, require regular assessments of safety glass performance. Compliance ensures that products can withstand specific impact forces. However, not all manufacturers conduct thorough testing to verify their claims. This creates a gap in the market where safety might be compromised. Awareness and stringent regulation are vital. They push manufacturers to prioritize quality and safety features.
The safety glass market is evolving rapidly. Innovations in materials are driving significant changes. Manufacturers are now focusing on durability and clarity. New composites enhance strength while maintaining lightweight properties. These advancements are crucial in construction and automotive industries.
Market trends indicate a growing demand for laminated glass. This type provides better impact resistance and sound insulation. It is widely used in modern buildings and vehicles. However, some challenges remain. The production processes can be costly. As demand rises, companies must balance efficiency and quality.
Additionally, recycled materials are gaining traction. This trend promotes sustainability within the industry. While the benefits are clear, the implementation can be tricky. Finding the right balance between recycled content and safety standards requires careful consideration. Continuous research and development are essential to address these challenges. Innovation in safety glass materials is vital for future applications.
| Glass Type | Features | Applications | Market Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tempered Glass | Highly durable, break-resistant. | Windows, shower doors, and glass doors. | Increasing demand in residential and commercial buildings. |
| Laminated Glass | PVB interlayer for safety, sound insulation. | Skylights, auto windshields, and facades. | Growing use in architecture for enhanced safety. |
| Bulletproof Glass | Multi-layered for resistance against bullets. | Banks, military vehicles, and secure facilities. | Rising security concerns driving growth. |
| Frosted Glass | Translucent, provides privacy. | Office partitions, bathroom windows. | High demand for modern design aesthetics. |
| Smart Glass | Adjusts light and heat transmission. | Commercial buildings, automotive applications. | Innovations in energy efficiency driving growth. |
| Insulated Glass | Energy-efficient, thermal insulation. | Windows in residential and commercial buildings. | Growing market due to focus on sustainability. |
| Wire Glass | Embedded wire offers fire resistance. | Fire rated doors and windows. | Constant requirement in safety regulations. |
| Ceramic Glass | High thermal resistance. | Fireplaces, stoves. | Niche applications driving steady demand. |
| Low-iron Glass | High clarity and light transmission. | Architectural marvels, solar panels. | Expanding use in premium constructions. |





